
Business of Banking
Bank:
Bank is a financial institution in which it accepts deposits for the purpose of providing loans and advances. It had done lending activities either direct or indirect manner through capital markets.Banks are highly regulated institutions in all over the world due to the importance of financial stability. Based on the international set of capital standards, banks had their minimum capital requirements known as Basel Accords and also based on fractional reserve banking it had maintained their liquid assets equal to only the portion of their current liabilities.
Background:
Banks began their careers from barter system only. Barter system means a system of providing grain loans to farmers and traders who had carried their goods between cities. This system began in 2000 BC. The ancient periods of China and India had shown the evidence for lending activities. The origin of modern banking was traced at medieval and early Renaissance Italy to their rich cities in the world. The earliest known state deposit bank was a bank of St. George founded in 1407 at Genoa, Italy. In modern banking practices including fractional reserve banking and issuing banknotes were emerged at 17 Th and 18 Th centuries. All the merchants were started to store gold with the goldsmiths of London who had provided private vaults and charged the free cost of services to their customers. The Bank of England was first to begin the permanent issue of banknotes in 1695 and The Royal Bank of Scotland began issues overdraft facility in 1728.Banking Business:
"Banking business" means the business of receiving money on current or deposit account, paying and collecting cheques drawn by or paid in by customers, the making of advances to customers, and includes such other business as the Authority may prescribe for the purposes of this Act. Banking business means the business of either or both of the following:- Receiving from the general public money on current, deposit, savings or another similar account repayable on demand or within less than [3 months] ... or with a period of call or notice of less than that period;
- Paying or collecting cheques drawn by or paid in by customers.
Banking Activities:
Banking activities are as follows – Personal banking, corporate banking, investment banking, private banking, transaction banking, insurance, consumer finance, foreign exchange trading, commodity trading, trading in equities, money market trading and futures and options tradings.Banking Channels:
Nowadays, banks were offered number of channels to their customers – branch, in-person banking, automated teller machine banking and bank by mail, online banking, mobile banking, telephone banking, video banking, relationship management, direct selling agency and cross-selling agency.Banking Models:
Banks were generated their fun ds from charging interest, transaction fees and financial advices. Through this the banks could got their profits by way of the level of interest on deposits and other sources of funds and the level of interest on lending activities.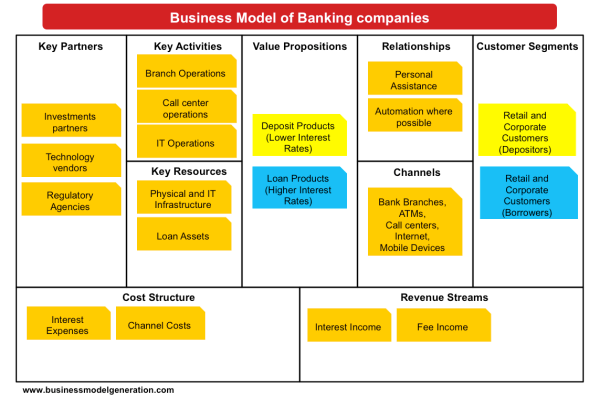
Banking Products:
- At Retail banking: - Savings account, Recurring deposit account, Fixed deposit account, Money market account, Certificate of deposit (CD), Individual retirement account (IRA), Credit card, Debit card, Mortgage, Mutual fund, Personal loan, Time deposits, ATM card, Current accounts, Cheque books, Automated Teller Machine (ATM).
- At Business/ commercial/ investment banking: - Business loan, Capital raising (equity / debt / hybrids), Revolving credit, Risk management (foreign exchange (FX)), interest rates, commodities, derivatives), Term loan, Cash management services (lock box, remote deposit capture, merchant processing), Credit services.

